Nagios Overview
Ethan Galstad envisioned a modular monitoring system in 1999, sparking collaborative development among early web forum programmers.
Originally named Netsaint, the project rebranded to Nagios in 2002 due to legal challenges, adopting a recursive acronym meaning "Nagios Ain’t Gonna Insist On Sainthood."
Galstad authored the core system while community volunteers contributed freely developed extensions known as plugins.
Establishing Nagios Enterprises LLC in 2007, Galstad transitioned both the core and the community-built plugin library into proprietary ownership.
This move catalyzed multiple forks as developers replicated the code, spawning enduring alternatives like Icinga, Checkmk, and Naemon.
To navigate market saturation, Nagios Enterprises preserved Nagios Core as free open-source software while launching Nagios XI as a premium commercial product.
The plugin repository evolved into Nagios Exchange, maintaining open access for community contributions.
Headquartered in St. Paul, Minnesota, the company balances open-source foundations with enterprise solutions.
Key offerings include Core for fundamental monitoring and XI for advanced features like centralized dashboards and log analysis.
Nagios expanded capabilities to cover cloud infrastructure and containerized environments, integrating AI-driven anomaly detection by 2023.
Privately held and founder-led, the organization prioritizes strategic autonomy under Galstad's continued leadership as CEO.
Global operations are facilitated through digital channels and partner networks rather than physical international offices.Nagios is a versatile IT infrastructure monitoring solution that caters to a diverse range of businesses and organizations. Its adaptable architecture, combined with both open-source and commercial options, makes it suitable for entities from small businesses to large enterprises in various sectors.
Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) often seek cost-effective and customizable monitoring solutions. These companies usually have limited budgets and cannot afford expensive, enterprise-level monitoring tools.
Large enterprises, on the other hand, need comprehensive monitoring capabilities across multiple geographic locations, hybrid cloud environments, and complex IT infrastructures. They require high performance, scalability, real-time alerts, and a wide array of integration options.
Industries such as banking, telecommunications, retail, healthcare, manufacturing, and IT services frequently rely on Nagios to monitor their critical infrastructure. Managed Service Providers (MSPs) use Nagios to offer outsourced IT services, requiring reliable, centralized monitoring to manage their clients' IT environments. MSPs typically handle multiple clients from a single location and need multi-tenant capabilities.
Government agencies and public sector organizations also depend on Nagios for reliable monitoring of their critical infrastructure. These entities manage sensitive data and require enhanced security, compliance, and high uptime.
Academic institutions, including universities, colleges, and research centers, manage extensive networks of computers, data centers, and services. Cost constraints make open-source solutions, like Nagios, particularly appealing for these institutions.
Cloud providers and data centers need to monitor infrastructure that spans physical, virtual, and cloud-based environments. This includes monitoring hardware, such as data center equipment, and virtual environments, such as cloud services, VMs, and containers.
DevOps and IT operations teams require real-time monitoring, alerting, and automation to ensure application performance and high availability. They often need integrations with CI/CD pipelines and tools for automated incident response.
Nagios has a global customer base that includes:
- Fortune 500 companies : Major corporations in finance, telecommunications, and manufacturing use Nagios for their enterprise monitoring needs.
- Tech companies : Leading IT companies and service providers, especially those in cloud services and SaaS, rely on Nagios for their IT infrastructure.
- Government and public agencies : National governments and public institutions use Nagios to monitor critical infrastructure and comply with regulatory requirements.
- Academic institutions : Universities and research centers worldwide use Nagios for network and application monitoring across their campuses and labs.
- SMEs and startups : Smaller organizations and startups favor Nagios due to its open-source version and scalability.
For smaller organizations or those with skilled IT teams, the open-source nature of Nagios Core provides a powerful and free monitoring solution. Larger businesses can benefit from advanced features in Nagios XI, such as reporting, dashboards, and customer support. Additionally, products like Nagios Log Server and Network Analyzer address more specific monitoring needs.
Nagios' architecture supports scalability, making it attractive to enterprises and MSPs managing multiple environments. Its plugin architecture and extensive third-party integrations allow for customization to meet specific monitoring needs across various industries and environments.
In summary, Nagios offers a broad market reach, catering to multiple industries and organization sizes. It provides both free and commercial options to meet different operational and financial requirements.
Nagios XI, the premium commercial offering from Nagios Enterprises, is a comprehensive monitoring and management solution for IT infrastructure. It builds on the robust foundation of the open-source Nagios Core, adding enhanced features, improved usability, and dedicated support for enterprise environments. Here’s a detailed exploration of Nagios XI, its key features, benefits, and use cases.
Key Features:
- User-Friendly Interface: Nagios XI boasts a modern, intuitive web interface that simplifies navigation and monitoring tasks.
- Customizable Views: Users can create personalized dashboards with widgets to monitor critical metrics, graphs, and alerts in real-time.
- Multi-Environment Support: It monitors a wide array of devices and services, including servers, network devices, applications, and cloud services.
- Agent and Agentless Monitoring: Supports both agent-based and agentless monitoring, providing flexibility in how devices are monitored.
- Configurable Alerts: Users can set up alerts through various channels, such as email, SMS, and integrations with communication tools like Slack and PagerDuty.
- Powerful Reporting Tools: Offers advanced reporting features for detailed performance reports, historical data analysis, and SLA tracking.
Nagios XI, first released in 2009, is designed for medium to large enterprises, IT service providers, and organizations needing robust monitoring solutions with user-friendly interfaces and extensive support. It can be deployed on-premises or in cloud environments, catering to diverse infrastructure needs.
Benefits:
- Enhanced Visibility: Provides a holistic view of the entire IT infrastructure, enabling proactive issue identification and resolution.
- Reduced Downtime: Real-time monitoring and alerting help organizations respond quickly to incidents, minimizing downtime and its impact on business operations.
- Improved Performance Management: Historical data and performance reports enable trend analysis, resource optimization, and future capacity planning.
- Cost-Effective Solution: Despite being a commercial product, Nagios XI offers a cost-effective monitoring solution compared to many other enterprise-grade options, especially considering its feature depth and support.
- Compatibility with Nagios Plugins: Leverages over 10,000 community-contributed plugins to extend monitoring capabilities.
- Custom Plugins: Users can develop their own plugins to monitor specific services or applications not covered by standard plugins.
- Optimized for Large Deployments: Efficiently handles large-scale environments, allowing the monitoring of thousands of devices and services.
- Distributed Monitoring: Supports distributed monitoring through remote instances, making it ideal for geographically dispersed infrastructures.
- Easy Setup: Configuration wizards simplify setup for common monitoring scenarios, making it accessible for users with varying levels of expertise.
- Not Available as a SaaS Platform: Does not run natively on Windows without a VM.
Nagios provides a system of templates that, when selected, adapted, and activated, apply a consistent security policy across a network. The package integrates seamlessly with various IT tools and services, such as ticketing systems, automation tools, and cloud services. Additionally, Nagios offers a RESTful API for developers to build custom integrations and automate workflows.
Nagios Enterprises provides enterprise-level support, including phone and email assistance, ensuring quick issue resolution. Users have access to extensive documentation, online training courses, and certification programs to maximize their use of Nagios XI.
Use Cases:
- IT Infrastructure Monitoring: Organizations use Nagios XI to monitor the health and performance of servers, network devices, and applications to ensure optimal performance and uptime.
- Cloud and Hybrid Environment Monitoring: Nagios XI supports monitoring for cloud services and hybrid environments, making it suitable for organizations with cloud-based applications and infrastructure.
- Managed Service Providers (MSPs): MSPs leverage Nagios XI to monitor multiple clients’ IT environments from a centralized dashboard, providing a comprehensive view of service availability and performance.
- Security Monitoring: Nagios XI can be configured to monitor for unusual activities or security breaches within the IT environment, enhancing an organization’s security posture.
- Performance Optimization: By analyzing historical performance data, organizations can optimize their IT resources, ensuring applications run smoothly and efficiently.
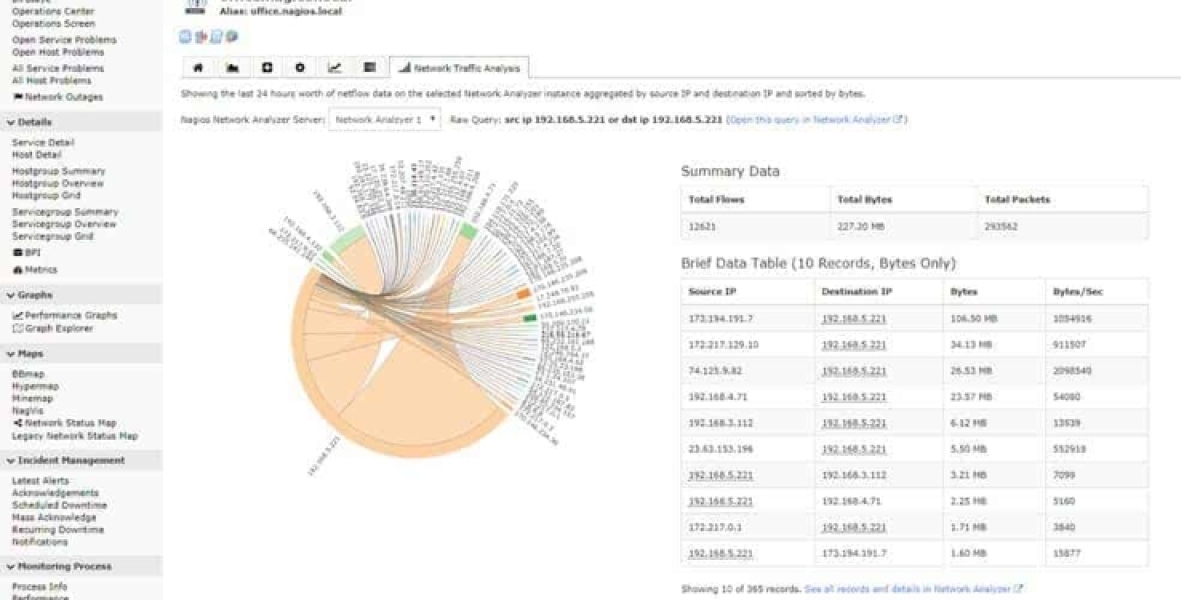
Nagios Network Analyzer:
Nagios Network Analyzer is a powerful tool that provides deep insights into network traffic. It helps organizations monitor bandwidth usage, detect security threats, and troubleshoot network issues. With its intuitive web-based interface, it captures, analyzes, and stores network flow data (such as NetFlow, sFlow, jFlow, and IPFIX) in real-time, offering clear views of traffic patterns and usage trends.
Advanced reporting and alerting capabilities make it easy to track specific traffic types, identify potential bottlenecks, and ensure critical services are not impacted by network slowdowns or malicious activity. One of the key benefits is its integration with the broader Nagios ecosystem, complementing the monitoring capabilities of Nagios XI and Nagios Core. This integration enables centralized management of both network and system monitoring, providing a unified view of an organization’s IT infrastructure.
Nagios Log Server:
Nagios Log Server is an enterprise-grade solution for log management and analysis. It centralizes, stores, and analyzes log data from across an organization’s IT infrastructure. With its easy-to-use web interface, users can query and visualize log data in real-time, enabling efficient troubleshooting and fast identification of potential issues, such as application errors, security threats, or system failures.
The package supports a wide range of log formats and sources, including servers, applications, and network devices, making it a comprehensive tool for managing logs from diverse systems in a single platform. Alerting and reporting capabilities allow administrators to set up custom alerts based on specific log patterns or conditions, making it easier to proactively address issues before they escalate. The system handles large volumes of log data by distributing the load across multiple instances. When integrated with other Nagios products, it provides a powerful, unified view of both system performance and security, offering a complete solution for infrastructure monitoring and management.
Competitors:
- Zabbix: An open-source monitoring tool known for its scalability and flexibility. It monitors a wide range of metrics, including networks, servers, cloud services, and applications. Features include real-time performance monitoring, alerting, and customizable dashboards. It supports distributed monitoring and integrates with popular tools like Grafana.
- Prometheus: An open-source monitoring tool designed for reliability and scalability in cloud-native environments. It is part of the Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF) and is widely used for monitoring Kubernetes clusters and microservices. It provides time-series data, event-based monitoring, and a powerful querying language called PromQL. It integrates with Grafana for data visualization.
- Icinga: An open-source monitoring tool that originated as a fork of Nagios. It offers similar monitoring capabilities but with a more modern architecture and interface. Icinga monitors networks, cloud services, and infrastructure, and it supports distributed monitoring. It has a web-based interface and better integration options compared to Nagios Core.
- Zenoss: An IT monitoring platform that combines network, server, and application monitoring in a unified tool. It is known for its hybrid IT infrastructure monitoring capabilities, offering event correlation, predictive analytics, and root-cause analysis.
- Checkmk: An open-source and enterprise-level IT monitoring tool. It offers comprehensive monitoring for servers, networks, containers, cloud infrastructure, and applications, with a focus on scalability and ease of use. Known for low resource consumption, even in large environments, Checkmk excels in auto-discovery features, reducing the need for manual configuration.
Open Source to Business Transition
Navigating Open Source to Commercial: The Nagios Journey
When Ethan Galstad transitioned Nagios from a community project to a commercial enterprise, it created significant ripples throughout the tech community. This transformation, while controversial at the time, represents a common path for successful open source projects seeking sustainability.
Many monitoring and logging solutions have followed similar trajectories - ElasticStack, Splunk, Graylog, and CheckMK all eventually faced the challenge of balancing free community offerings with revenue-generating business models.
Despite initial community concerns about Nagios Enterprises taking the system private, the company successfully maintained both commercial and open source versions. This dual approach has ensured the continued development of the free community edition while supporting the company's growth through premium offerings.
The Nagios case study demonstrates how open source projects can evolve into commercial entities while still honoring their community roots - a delicate balance that continues to challenge technology innovators today.
What is a Netflix VPN and How to Get One
A Netflix VPN is a specialized virtual private network service that enables viewers to bypass geographical restrictions on streaming content, allowing access to different regional libraries of shows and movies not normally available in their location. By connecting to servers in various countries, users can unlock a wider selection of entertainment options that would otherwise be inaccessible due to licensing agreements and content distribution rights. Netflix VPN services have become increasingly popular among international travelers and content enthusiasts who wish to maintain access to their favorite programs regardless of where they physically reside.
Why Choose SafeShell as Your Netflix VPN?
If you're looking to access region-restricted content by Netflix VPN, you may want to consider the SafeShell VPN for its exceptional performance and features. When your Netflix vpn not working due to outdated software or detection mechanisms, SafeShell VPN offers a reliable solution with numerous advantages:
- High-speed Servers - SafeShell provides optimized servers specifically designed for Netflix streaming, ensuring buffer-free playback and high-definition viewing experience.
- Multi-device Support - Connect up to five devices simultaneously across various platforms including Windows, macOS, iOS, Android, and smart TVs.
- Innovative App Mode - Uniquely access content from multiple regions concurrently, expanding your entertainment options beyond a single geographic library.
- Unmatched Speed - Experience superior streaming without buffering or throttling issues, as SafeShell VPN delivers exceptional connection speeds with no bandwidth restrictions.
- Enhanced Security - Benefit from the proprietary "ShellGuard" protocol that safeguards your browsing activities with advanced encryption technology.
- Risk-free Trial - Test all premium features with a flexible free trial plan before making any commitment, allowing you to verify its performance with Netflix firsthand.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Watch Netflix with SafeShell VPN
To begin using SafeShell Netflix VPN , first secure your subscription by visiting the SafeShell VPN website and selecting the plan that aligns with your requirements. Proceed to download and install the official SafeShell VPN application suitable for your specific device operating system.
Once the app is installed, launch it and log into your account. For optimal Netflix streaming, navigate within the app to select the recommended APP mode. Then, browse the list of available VPN servers and choose one located in the country whose Netflix library you wish to access.
After connecting to your chosen server, simply open your Netflix app or navigate to the Netflix website in your browser and log in. You should now have seamless access to the region-specific Netflix content library corresponding to your selected SafeShell Netflix VPN server location.